Why Straw?
Straw is a material source that has been used for centuries for building construction. In the US, straw bale building was first developed in Nebraska in the 1880’s due to lack of available timber. In the 1920’s, people in France designed panels made of packed straw in wooden frames. In 2015, after 20 years of concerted effort by the straw bale building community, strawbale construction was successfully included in the International Residential Code. Straw is typically used for construction as tightly bound in bales, packed into prefabricated panels or used as blown-in insulation.
Straw is a byproduct of food production. When cereal crops such as wheat, rice, barley, corn, oat and rye are harvested, the remaining stalks of the plant become straw. After harvesting, it is sun-dried, a method that allows nitrogen levels to decrease and impede degradation of the material. When it’s not used in buildings, straw can be used for mulch, animal bedding, and fuel. But it is often burned to expedite its disposal and when it burns , stored carbon is released, letting a valuable resource go to waste.
“Straw stores sixty times more carbon than used to grow, bale, and transport to building sites in the same region.”
Benefits of Straw Construction
Using straw as a major ingredient for building materials dramatically reduces both the need for toxic chemicals and carbon emissions typically embodied in materials. Densely packed straw reduces available oxygen, ensuring fire resistance and avoiding the need for toxic flame retardant chemicals. Rice straw in particular contains a higher content of silica which acts as a natural fire retardant and prevents mildew. Straw panels used as insulation replace toxic foams and batt insulation materials which contain formaldehyde and isocyanates that are harmful to human health.
Straw stores a significant amount of carbon, so using it for building materials contributes to our global Emission Reduction Goals. According to the Carbon Smart Materials Palette, “straw stores sixty times more carbon than used to grow, bale, and transport to building sites in the same region.”
Combined with organic, regenerative agriculture techniques, utilizing straw bales and packed straw for building can increase the amount of carbon storage and remove pesticides & fertilizers that harm ecosystems. Institutions such as the Savory Institute assess farms for their impacts on soil health and biodiversity.

IStraw’s Elite GREENLINE straw is free of pesticides.
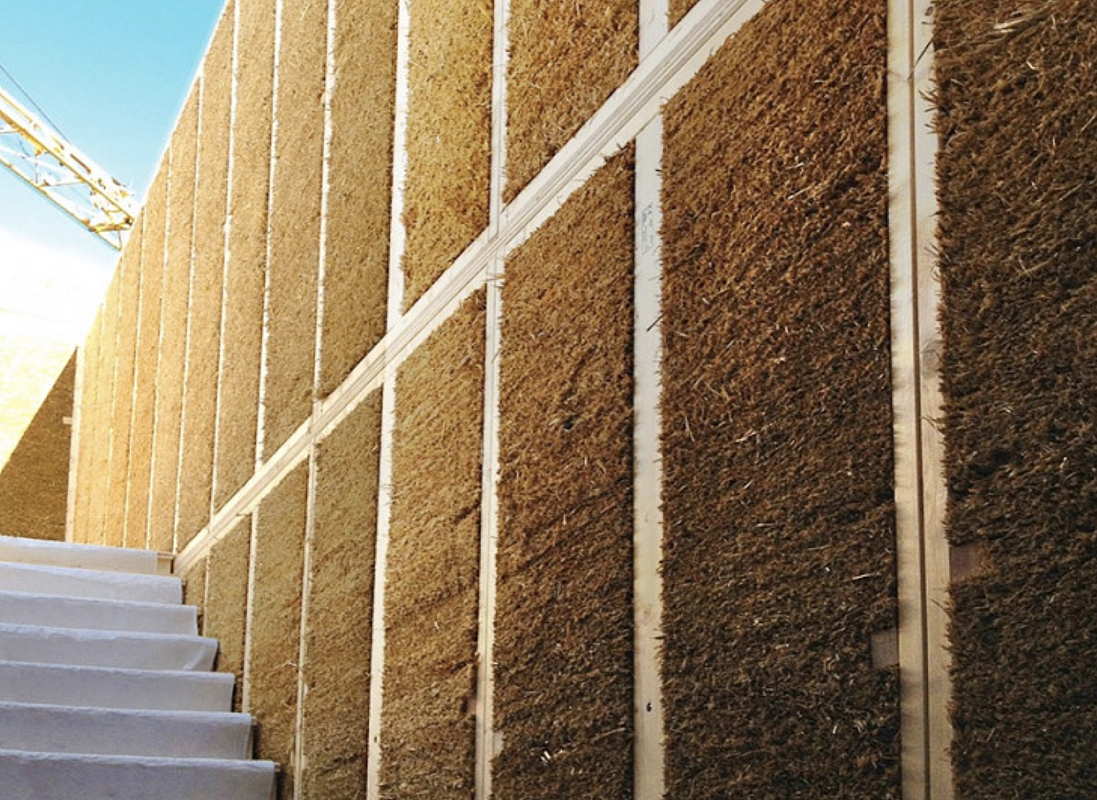

EcoCocon Straw Panels

Wall Assemblies by Croft
Components for Successful Straw Construction
Straw works well with clay and/or lime plaster. It allows breathability and moisture regulation as well as prevents mold and mildew. Controlling moisture is a key to success when building with straw. The optimal moisture content range is between 18-25% dry basis, 20% wet basis according to research “How Straw Decomposes” by the EcoBuild Network. The moisture can be tested prior to installation using a moisture probe. If moisture exceeds these values, decomposition, mold, and mildew can occur. New Frameworks recommends using a secondary air barrier any place the plaster meets a wood edge to seal gaps and ensure air tightness.
When building wall assemblies, it’s important to use FSC-certified wood to ensure safe logging practices and formaldehyde-free plywood to reduce exposure to toxic binders. Croft uses Roseburg, a company known to use lower content of petrochemical resin binders than other manufacturers. Their MDF has been vetted and included within the HML Material Collection on Composite Wood Products.
Looking Forward
The use of straw construction has been revitalized in several countries, including France. HML hosted French architect Martin Paquot (member of the French Network for Straw Bale Construction) in November 2023 to share current construction techniques and institutional projects utilizing straw for buildings in and around Paris. Paquot’s presentation highlighted the use of a range of bio-based materials and discussed France’s introduction of a Straw Bale Building Code in 2012. Since then, over 10,000 straw bale buildings have been completed in France.
Since 2012, over 10,000 straw bale buildings have been completed in France.
Agriboard is a manufacturer with a patented manufacturing system for producing compressed agricultural fiber board. They see the potential use of straw to build affordable housing. The company has collaborated with groups in Haiti, Sri Lanka, and Mexico to provide aid after natural disasters. Their website provides useful information on regions around the world, where wheat and rice straw is abundantly available.
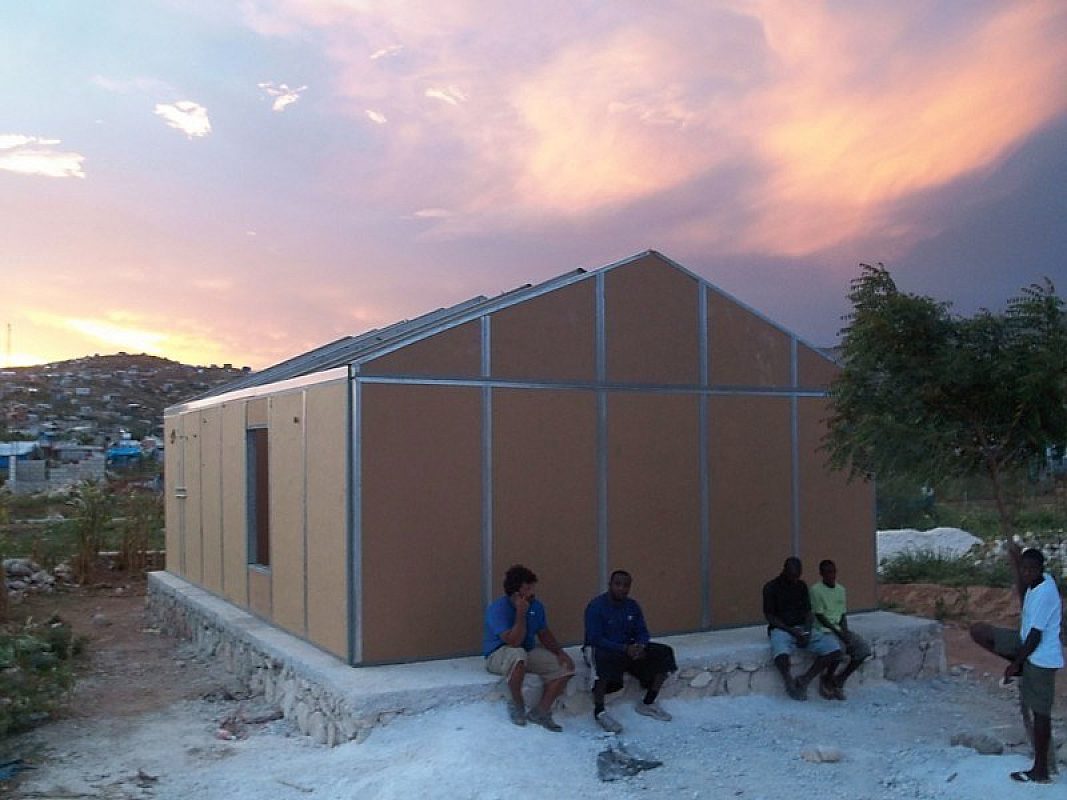

Agriboard Straw Building in Haiti
Straw is used to build affordable housing
Designing with Plant-Based Materials
Designing with plants requires a mindset for thinking holistically about where materials come from. Plant-based materials are naturally tied to regional landscapes. Connections between the creative intent of the architect or designer and the work of farmers or laborers in harvesting, processing and building become more evident. Each project is highly specific, based on local agricultural waste and available knowledge. It is essential to consult and collaborate with natural builders for the project to benefit from their expertise and best practices. For more details, refer to the straw-based products featured in the HML Material Collection, Plant.
For more information on Straw, refer to New Frameworks’ book, “Natural Building Companion” and the CASBA book “Straw Bale Building Details.”
Straw Panel Manufacturers Around the World
In the latest issue of The Last Straw, a magazine focused on natural building methods, the editorial team composed an informative and clear graphic of pre-fabricated Straw Panel Manufacturers Around the World. This includes manufacturers whose product is available on the market as well as those who are in development, as of 2024. They also include an informative chart with the size, thickness and weight of the panels, as well as the R-value and fire performance of the 18 different products. Kudos to the editorial collective, Zoe Gardner, Kenny Fallon Jr. and Gavin Fraser, for visualizing the availability of prefab straw panels. It’s encouraging news and underscores the potential for widespread acceleration of healthier insulation, and healthier buildings.
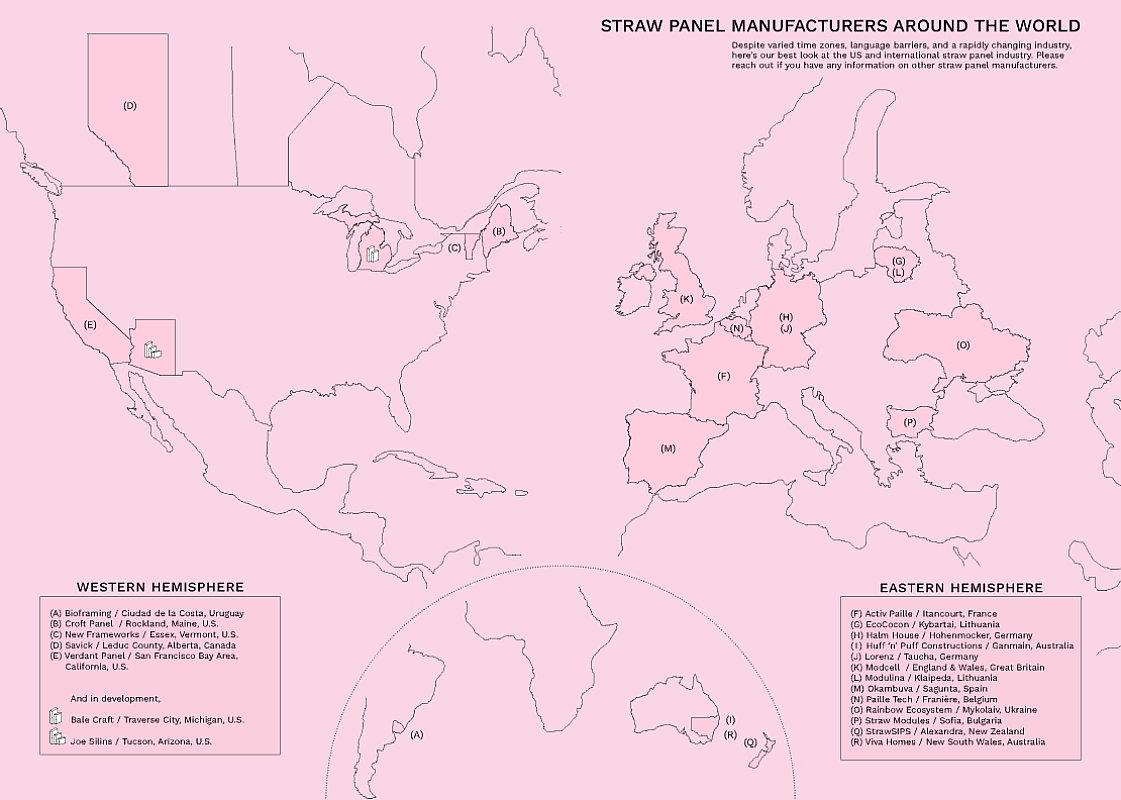
Straw Panel Manufacturers Around the World, image courtesy of The Last Straw, issue no. 75, Beyond the Bale
Read More
Join Our Academic Network
Get Access to our carefully researched and curated academic resources, including model syllabi and webinars. An email from an academic institution or a .edu email address is required. If your academic institution does not use .edu email addresses but you would like to join the network, please contact healthymaterialslab@newschool.edu.
Already have an account? Log in